| |
MPLS is able to
work in an environment that uses any data link technology,
connection-oriented and connectionless. MPLS also provides the
potential for all traffic to be switched, but this depends on the
granularity of label assignment, which again is flexible and depends
on the approach used to identify traffic (discussed above). Labels
may be assigned per address prefix (e.g., a destination network
address prefix) or set of prefixes, and can also represent explicit
routes.
On
a finer-grained level, labels can be defined per host route and also
per user. At the lowest level, a label can represent a combined
source and destination pair, and in the context of RSVP can also
represent packets matching a particular filter specification.
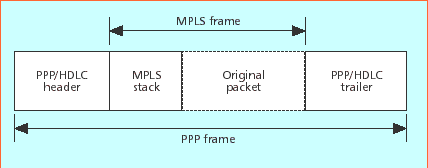
Figure 12 - MPLS
encoding for PPP/HDLC over SONET/SDH links
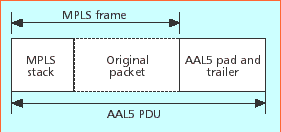
Figure 13 - MPLS
encoding for ATM links
Currently, MPLS
forwarding is defined for a range of link layer technologies, some
of which are inherently label-switching (e.g., ATM and frame relay,
FR) and others are not, such as packet over SONET/SDH-POS, Ethernet,
and DPT. A number of encapsulation schemes are in Figure 12 and 13.
|
|